Building Java Programs
Lab: Classes and Objects
Except where otherwise noted, the contents of this document are Copyright 2019 Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp.
Modified by T. W. Bennet
Lab goals
Goals for this problem set:
- write our own new classes of objects
- declare fields, methods, and constructors
- understand the difference between class code and client code
Declaring a class (syntax)
public class ClassName {
// fields
fieldType fieldName;
// methods
public returnType methodName() {
statements;
}
}
A couple things look different than programs for past homeworks:
- no
mainmethod. It won't be run like a client program. - methods don't have the
statickeyword in the header. - variables declared outside of any method (fields) are visible in every method.
Exercise : Client code method call syntax

Suppose a method in the BankAccount class is defined as:
public double computeInterest(int rate)
If the client code has declared a BankAccount variable named acct, which of the following would be a valid call to the above method?
Exercise : PointClient
-
Download the following files
 Point.java
and
Point.java
and
 PointClient.java
to your machine and open them with your editor.
PointClient.java
to your machine and open them with your editor.
-
The
PointClientprogram is supposed to construct twoPointobjects, translate each, and then print their coordinates. Finish the program so that it runs properly. (You don't need to modifyPoint.java.)
Point and PointMain
-
Download the following file
 PointMain.java
to your machine and open it with your editor.
PointMain.java
to your machine and open it with your editor.
-
In the next several exercises, you will edit
Point.javaand add several methods. ThePointMainprogram calls these methods; you can use it to test your code. Initially, these tests are commented out. As you add each method toPoint, uncomment the test inPointMain.java.
Exercise : Make Point Comparable.
- Modify
Point.javato make thePointclass implement theComparableinterface. APointshould be comparable to anotherPoint. - Implement the required
CompareTomethod to satify theComparableinterface. If the x values of the two points differ, the order of the points is the order of the x values. If the x values match, the order is that of the y values. Of course, if the x values and y values each match, the points are equal
Exercise : quadrant
Add the following method to the Point class:
public int quadrant()
Returns which quadrant of the x/y plane this Point object falls in.
Quadrant 1 contains all points whose x and y values are both positive.
Quadrant 2 contains all points with negative x but positive y.
Quadrant 3 contains all points with negative x and y values.
Quadrant 4 contains all points with positive x but negative y.
If the point lies directly on the x and/or y axis, return 0.
Test your code by uncommenting the quadrant tests in
PointMain, recompile, and rerun the program.
Exercise : flip
Add the following method to the Point class:
public void flip()
Negates and swaps the x/y coordinates of the Point object.
For example, if an object pt initially represents the point (5, -3), after a call of pt.flip(); , the object should represent (3, -5).
If the same object initially represents the point (4, 17), after a call to pt.flip();, the object should represent (-17, -4).
Note carefully: the method both exchanges the x and y values, and changes the sign of each one.
Test your code by uncommenting the code in PointMain for testing flip, and running the program again.
Rectangle class
Suppose you are given a class named Rectangle with the following contents:
// A Rectangle stores an (x, y) coordinate of its top/left corner, a width and height.
public class Rectangle {
private int x;
private int y;
private int width;
private int height;
// constructs a new Rectangle with the given x,y, width, and height
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int w, int h)
// returns the fields' values
public int getX()
public int getY()
public int getWidth()
public int getHeight()
// returns a string such as {(5,12), 4x8}
public String toString()
...
}
Exercise : Rectangle Class
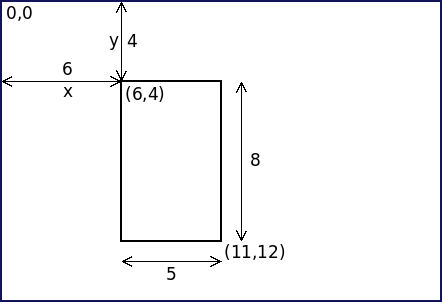 Rectangles are represented by the position of their upper left corner, and by their
width and length. As common in computer image software, coordinates measure
distance to the right and
down from the top. The rectangle pictured is
Rectangles are represented by the position of their upper left corner, and by their
width and length. As common in computer image software, coordinates measure
distance to the right and
down from the top. The rectangle pictured is {(6,4), 5x8}-
Create a file
Rectangle.java, and copy the code from the previous slide into it. - Complete the methods shown there as directed in the comments. Make sure the resulting code compiles.
-
Download the
 TestRectangle.java
file to test your method. Compile and run, and fix any errors.
TestRectangle.java
file to test your method. Compile and run, and fix any errors.
Exercise : Rectangle corners
-
Add four methods to
Rectangle: getUpLeft, getUpRight, getLowLeft, getLowRight. Each returns a Point representing the location of the appropriate corner. - Uncomment the appropriate portion of TestRectangle and test your method.
Exercise : Rectangle contains
-
Write an instance method
containsthat will be placed inside theRectangleclass. The method accepts integers for x and y as parameters and turnstrueif and only if that x,y coordinate lies within this rectangle. The edges are included; for example, a rectangle with x=2, y=5, width=8, height=10 will returntruefor any point from (2, 5) through (10, 15) inclusive. -
Create a second version of
contains, which takes a Point object as its argument and returns true if and only if the Point lies inside the rectangle in the same sense. Your second method should just call the first. - Uncomment the appropriate code in
TestRectangle.javato test your new methods
Exercise : Rectangle overlap
-
Write an instance method
overlapthat will be placed inside theRectangleclass. The method accepts anotherRectangle, and returns true of the two overlap, including sharing an edge or a corner. - The simplest way to do this is to test if any corner of one rectangle is contained in the other. Test each corners of one against the other, each way. If any is true, return true. Otherwise, return false.
- Uncomment the appropriate code in
TestRectangle.javato test your new method.