

Examples

- MS-DOS
- Linked files with a FAT.
- FAT is loaded into memory on mount.
- Size of offset has varied (bits): FAT-12, FAT-16, FAT-32 (which is
actually 28).
- Block size.
- Originally 512.
- Now configurable multiple, up to 4K.
- Max partition size is the block size times two to the offset size,
so have had to increase.
- Fixed-size directory entry
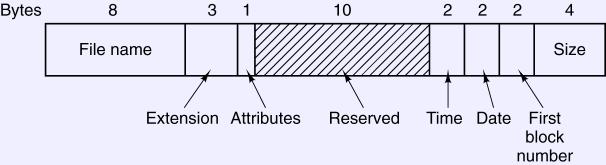
- Time is seconds, minutes, and hours.
- Date is day, month, and years since 1980.
- File names limited to 8 and 3.
- Windows 95 uses a trick to store longer names in successive
otherwise-unused entries.
- CD-ROM (ISO 9660)
- Format invented for music.
- Disk has blocks of 2048 bytes.
- Blocks are on a spiral, and can be identified by playing time,
75 blocks/second.
- Disk begins with fixed size block.
- 16 blocks for any use the creator desires.
- Primary volume descriptor: fields for system id, owner, etc.
- Parameters, such as block size.
- Directory entry for the root.
- Fixed-size directory entries.
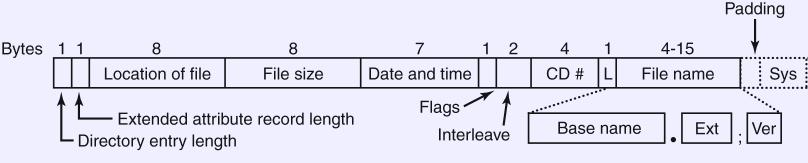
- Entries are alphabetical by file name, except the first two.
These are this directory and its parent.
- Files don't need to be in the same order.
- Location and size specify the file location, which is contiguous.
- Timestamp is separate bytes for year, month, day, hour, minute,
second, and time zone. Start at 1900.
- Flags denote directories, last entry, and other things.
- The CD# say which CD has the file. Sets are allowed.
- L is the length of the file name.
- Sys is whatever the system wants to do.
- Directories can only be nested to 8 levels.
- Levels vary the strictness.
- Level 1: 8/3 filenames, 8-char directory names, contiguous files.
- Level 2: Names to 31 characters.
- Level 3: Allows files to be non-contiguous, and data appearing
in multiple files may be recorded once.
- Extensions.
- Rock Ridge. For Unix systems.
- Uses the Sys field, since systems that don't understand will ignore
it.
- Series of fields recording what Unix needs to record.
- PX: POSIX attributes (Unix permissions).
- PN: Device number needed to record dev entries.
- SL: Symbolic link.
- NM: Alternative name, which is not subject to ISO restrictions.
- CL, PL, RE: Child location, Parent location, Relocation. This
creates an alternate tree structure to get around the depth
restriction.
- TF: Timestamps. The unix create, modify, and access.
- Joliet. For Windows.
- Longer file names, using Unicode characters.
- No nesting limit.
- Directory name extensions (just in case).
- Unix

