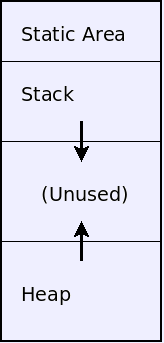
- Memory layout.
- Static area is allocated at compile time.
- Stack holds function activation and grows down.
- Heap holds dynamically-allocated areas and grows up.
- Variable-sized arrays.
- May be allocated on stack or heap.
- When on the heap, a dope vector may exist on the stack with dimensions and a pointer.
- Heap management.
- Simple free list.
- Buddy system.
- Dividing memory
- Powers-of-two free lists.
- Garbage Collection
- Let the programmer worry about it.
- Programmer must explicitly free memory when finished.
- Easy to forget.
- Particularly a problem when exceptions are caught.
try allocate a bunch of memory do stuff that might throw exceptions free the memory catch Now you have a bunch of garbage. end
- C++ auto_ptr
- Deletes the object when the pointer is destroyed.
- Not a general solution.
- Helpful for exceptions.
- Reference counting.
- Each allocated block keeps a count of how many pointers there are to it.
- Counts are updated whenever pointers are created or destroyed.
- If the count reaches zero, the block is freed.
- Fails for circular structures.
- Mark-and-sweep.
- Pointers on the stack are called roots.
- When you run out of memory:
- Recursively find and mark each block reachable from some root.
- Un-marked parts are garbage. Delete them.
- Marking is the hard part. The more you do, the less you get.
- Mark This.
- Copy collection.
- Divide memory into two equal parts. Allocate from one; other stays idle.
- When you run out of memory (from the active half):
- Recursively find each block reachable from some root, and copy it to the inactive half.
- Keep track of which blocks you've moved, and redirect all existing pointers to the new copies.
- Garbage naturally remains uncopied.
- Swap active sides.
- Copy this.
- Avoids extra space for counts or marks at the cost of half of memory.
- No free list, so no free list search needed for new allocations.
- Let the programmer worry about it.